Can a website owner see my browsing history?
Can a website owner see my browsing history on other websites?
A website can track which of its own webpages a user has visited, which probably isn’t too surprising.
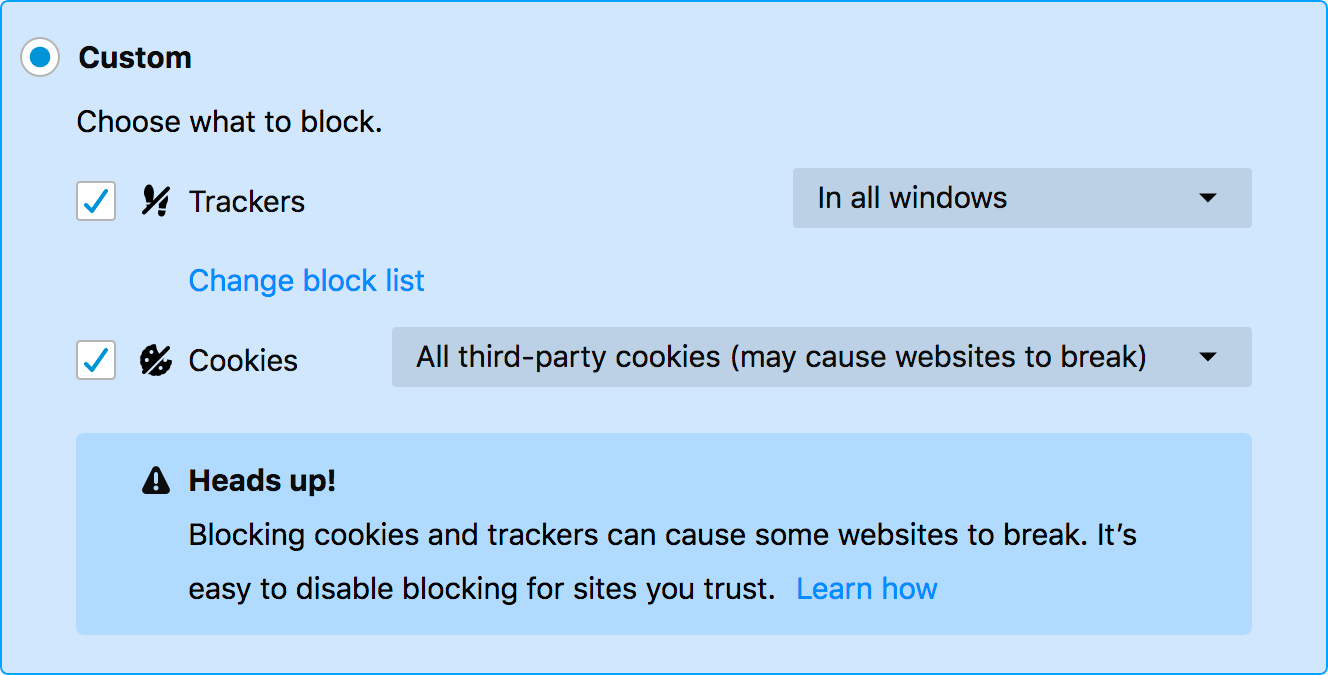
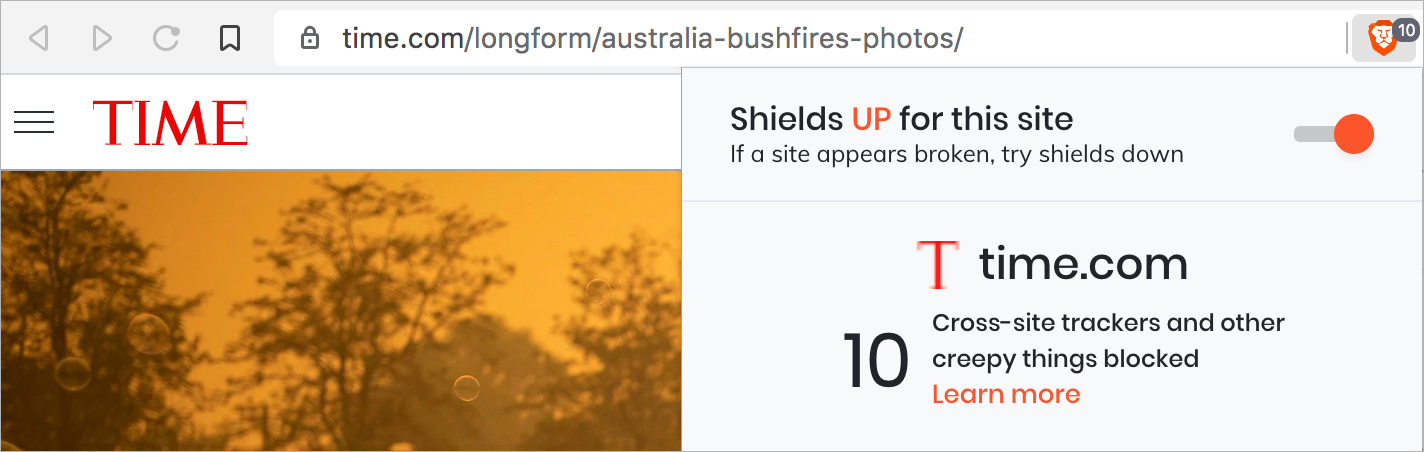
However, a website can also track a user’s browsing history across other websites by using third-party cookies, as long as each site loads the cookie from the same domain.
To prevent tracking across multiple websites, most browsers allow users an option to disable third-party cookies.
Alternatively, some browsers default to disallowing third-party cookies.
Browsers tracking browsing history
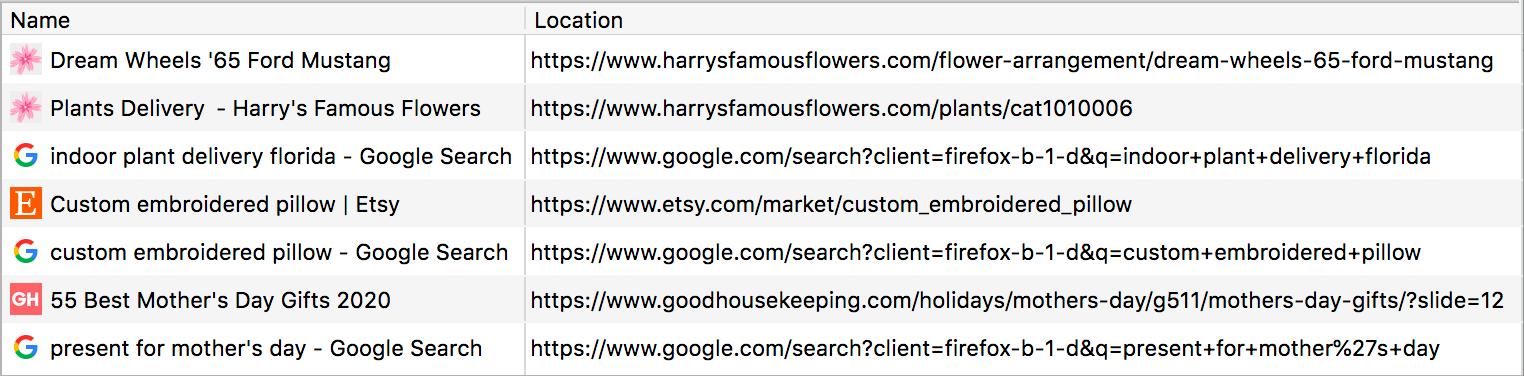
Browsers store the browsing history for us across the entire web, a feature that makes it easier to re-find websites we visited in the past and autocomplete URLs as we’re typing.
That handy feature means that anyone with access to our computer, like a parent, roommate, or classmate, can also see which websites we’ve visited.
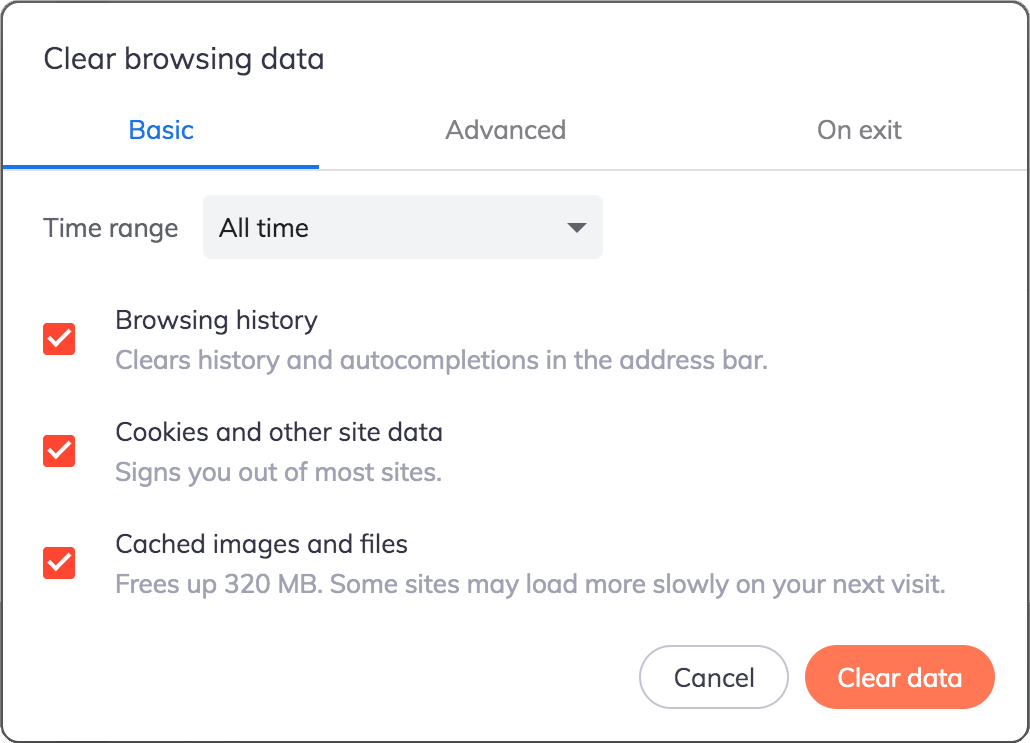
Most browsers give users options to clear the browsing history, however. In some browsers, you can even opt to clear the browsing history every time the browser restarts.
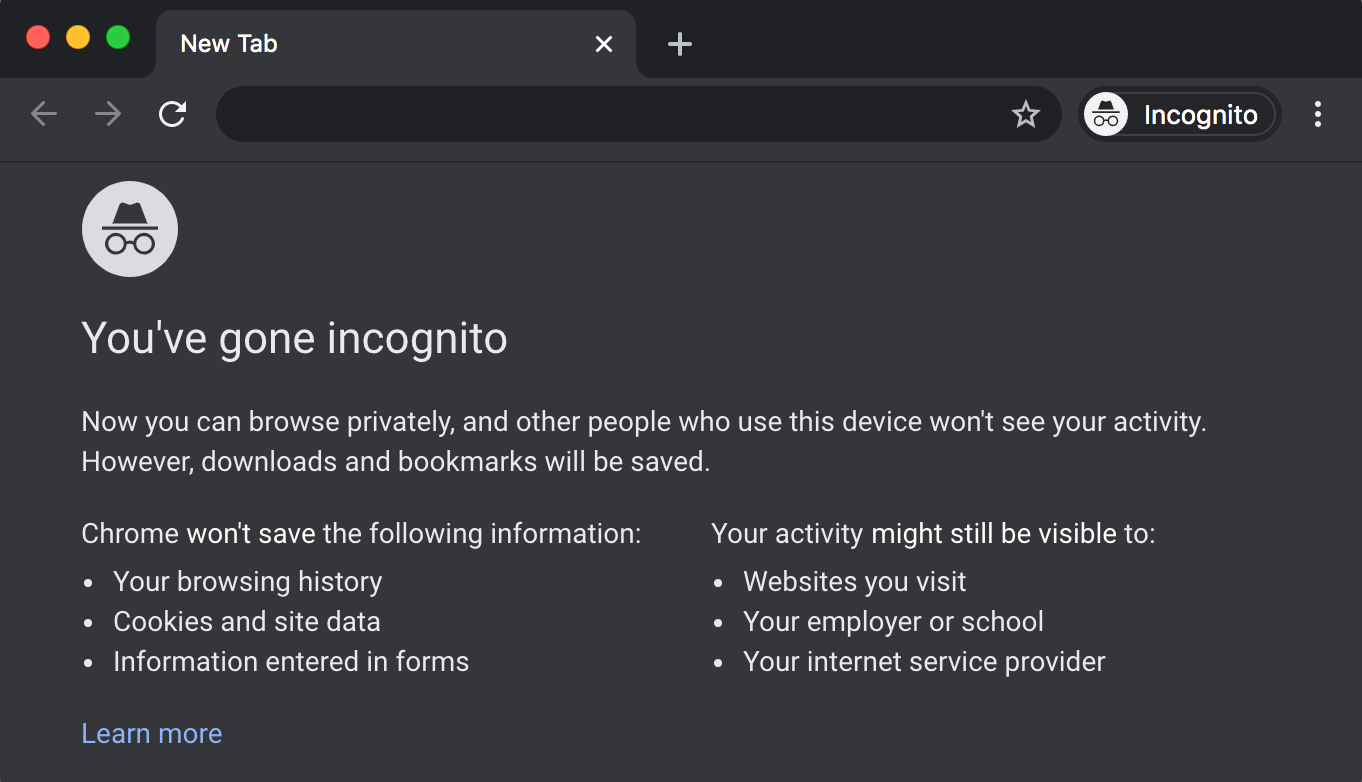
Many browsers also provide an incognito browsing mode, a new browser window that will not store browsing history at all. Once you close the window, it will also forget any cookies generated in that session.
Routers tracking browsing history
Anyone who can access the router that forwards a packet can monitor the destinations of HTTP requests.
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) administers the first routers that a packet travels through (excluding the home/office/school) router, so the ISP can see every HTTP request that’s sent through those routers. Users can use HTTPS-secured websites to hide the contents of their requests, but HTTPS will still reveal the domain names. ISPs can use that information to find customers that are engaged in illegal activities, such as downloading pirated movies.
But ISPs aren’t the only ones with access to routers. Government organizations have found various ways to gain access to routers and their forwarding data. In the US, the NSA reportedly installed backdoor surveillance monitoring programs on routers before they were exported to foreign customers. ^11start superscript, 1, end superscript
For governments, monitoring online activity can be a way to discover behavior that they consider dangerous or unwanted. For citizens, governmental monitoring may reduce their privacy and threaten their freedom of speech. Journalists have reported that it’s harder now to research stories about government activities, as their sources are afraid to communicate over the open Internet. ^22squared
Concerned users have a few options to increase the privacy of their browsing history.
One popular option, especially for journalists, is a Virtual Private Network (VPN). When using a VPN, the computer sends a packet of encrypted data with a destination of the VPN server to the ISP. The VPN server decrypts the data, finds out where the user actually wants to send the packet, and then forwards the packet to that destination.
The VPN server knows the user’s browsing history, but the ISP does not. Plus, other routers after the VPN will only see that the packet came from the VPN IP address, not from the user’s IP address. A VPN subscription is often expensive, however, and the additional stop along the way can result in a slower browsing experience. The benefits may outweigh the costs for journalists, but VPNs are not yet used by the standard web surfer.
Another option is Tor, an open source program for anonymizing Internet traffic. When using Tor, the computer sends an encrypted packet through a large number of volunteer relays. The data is packaged such that each relay only knows where it came from and where it’s going, and no relay knows both the sender IP address and the destination IP address.
Tor can provide truly anonymous browsing, but it also severely slows down the browsing experience, since it has to hop through volunteer relays that can be located anywhere on the Internet.
A final option is to lobby ISPs and governments to reduce their amount of monitoring or tighten their processes around accessing the browsing history of users. For example, the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is a non-profit that researches issues around digital privacy and tries to make changes through litigation, technology, and activism.